Custodial vs Non-custodial Wallets: Everything You Need to Know (2025)

Table of Contents
- TL;DR Summary
- What is a Crypto Wallet and How Does it Work?
- What is a Custodial Wallet?
- What is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
- Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallet: Complete Comparison
- Security Analysis: Which Wallet Type is Safer?
- Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
- Market Statistics and Adoption Trends
- When to Use Custodial Wallets
- When to Use Non-Custodial Wallets
- Advanced Wallet Technologies: MPC and Beyond
- Best Custodial Wallets in 2025
- Best Non-Custodial Wallets in 2025
- Cost Analysis: Custodial vs Non-Custodial
- Hybrid Approach: Using Both Wallet Types
- Future of Crypto Wallets
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- Glossary
TL;DR Summary
Custodial wallets are managed by third-party services like exchanges that hold your private keys, offering convenience and account recovery but requiring trust in the custodian.
Non-custodial wallets give you complete control over your private keys and funds but require personal responsibility for security and backup.
Key Statistics:
- Global crypto wallet market: $12.59 billion in 2024, expected to reach $100.77 billion by 2033
- Over 560 million crypto owners worldwide in 2024
- $2.2 billion stolen%20protocols%20remaining%20prime%20targets.) in crypto hacks in 2024, highlighting security importance
- Non-custodial wallet market growing at 24.3% CAGR
Quick Decision Guide
Choose custodial if: You're new to crypto, want convenience, need customer support, or prioritize ease of use.
Choose non-custodial if: You value complete control, use DeFi protocols, hold long-term investments, or prioritize maximum security and privacy.
-1752233239709.png)
What is a Crypto Wallet and How Does it Work?
A cryptocurrency wallet serves as your gateway to the blockchain, enabling you to store, send, and receive digital assets. Despite the name, crypto wallets don't actually "store" cryptocurrency in the traditional sense, instead, they store the cryptographic keys that prove ownership of your digital assets recorded on the blockchain.
Essential Wallet Components
Public Key: Your wallet address that others can use to send you cryptocurrency. Think of it as your bank account number completely safe to share publicly and often displayed as a long string of characters starting with specific prefixes depending on the cryptocurrency.
Private Key: The secret cryptographic code that proves ownership of your funds and authorizes transactions. This functions like your bank account password and must be kept absolutely secure. Anyone with access to your private key can control your funds.
Seed Phrase: A sequence of 12, 18, or 24 randomly generated words that serve as the master backup for your private keys. This phrase can restore access to your entire wallet on any compatible device, making it arguably the most important element of cryptocurrency security.
Hot vs Cold Storage
Hot wallets remain connected to the internet, making them convenient for frequent transactions and DeFi interactions. Popular examples include MetaMask browser extensions for Ethereum and DeFi activities, and Trust Wallet mobile applications for on-the-go trading.
Cold wallets store your keys offline, providing maximum security for long-term holdings. Hardware devices like Ledger Nano series offer the best balance of security and usability, while paper wallets represent the most basic form of cold storage.
The Fundamental Question
The core distinction between wallet types isn't technical but philosophical:
**Who controls the private keys that govern your digital assets? **
This question leads us to the essential difference between custodial and non-custodial approaches.
What is a Custodial Wallet?
A custodial wallet represents a trust-based approach where a third-party service provider holds and manages your private keys on your behalf.
This custodian, typically a cryptocurrency exchange or specialized wallet service, assumes responsibility for securing your funds while providing you with account access through traditional login credentials.
How Custodial Wallets Operate
The custodial model mirrors traditional banking relationships where you trust the institution to safeguard your assets.
When you create an account with major exchanges, you're essentially opening a digital account where the service manages blockchain interactions while you interact through their user-friendly interface.
Account Setup Process: Account creation involves standard online registration followed by identity verification through Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures. The service then generates and stores your private keys in their secure infrastructure, often using advanced security measures like hardware security modules and multi-signature protocols.
Key Custodial Features
Professional Security Management: Custodial services employ dedicated security teams, implement multi-layered security protocols, and undergo regular third-party audits. These professional measures often exceed what individual users can implement independently.
Account Recovery Services: Password recovery becomes possible through customer support, as the custodian can verify your identity and restore account access. This safety net prevents permanent fund loss due to forgotten credentials.
Insurance Protection: Many custodial services offer insurance coverage for digital assets, with leading exchanges providing up to $250 million in coverage for customer funds through both FDIC insurance for fiat holdings and specialized crypto insurance policies.
Integrated Financial Services: Custodial wallets typically include built-in trading, staking, lending, and other financial services, allowing users to seamlessly transition between different activities without managing multiple platforms.
Leading Custodial Wallet Examples
Coinbase stands out for strong US regulatory compliance and FDIC insurance for USD holdings, making it popular among American users seeking regulatory certainty.
Binance offers global reach and extensive trading features, serving as both exchange and wallet with comprehensive cryptocurrency support.
Kraken has built a reputation for security excellence and institutional-grade custody services, appealing to both retail and professional traders.
Gemini operates as a New York trust company with regulatory compliance focus, providing additional legal protections for customer assets.
What is a Non-Custodial Wallet?
A non-custodial wallet, also known as a self-custody wallet, puts you in complete control of your private keys and, by extension, your digital assets. No third party can access your funds, freeze your account, or control your transactions, embodying the cryptocurrency ethos of "not your keys, not your coins."
Self-Custody Operation
Wallet Generation: Creating a non-custodial wallet involves generating cryptographic keys locally on your device, ensuring that no external service ever accesses your private information. You receive a seed phrase that serves as the master key to your wallet, which you must store securely and never share.
Transaction Authorization: All transactions happen directly on your device, where they're cryptographically signed using your private keys before being broadcast to the blockchain network. This process ensures that only you can authorize fund movements, regardless of external circumstances.
Types of Non-Custodial Wallets
Software wallets offer convenience and functionality across different platforms:
Desktop Applications like Electrum and Exodus install directly on your computer, providing full-featured wallet capabilities with offline transaction signing options.
Mobile Applications such as Trust Wallet and Phantom bring crypto management to smartphones, enabling DeFi access and transaction capabilities on-the-go.
Browser Extensions like MetaMask integrate seamlessly with web-based decentralized applications, making DeFi protocols and NFT marketplaces easily accessible.
Hardware Wallets represent the gold standard for non-custodial security:
- Ledger Nano Series devices store private keys on specialized hardware isolated from internet-connected computers, requiring physical confirmation for transactions.
- Trezor Models offer similar security with user-friendly interfaces and open-source firmware that can be independently verified.
Core Self-Custody Principles
Complete Ownership: The fundamental principle means you bear full responsibility for asset security. Lost private keys or seed phrases result in permanent loss of access, with no customer support or recovery mechanism available.
DeFi Compatibility: Non-custodial wallets provide unrestricted access to decentralized finance protocols, yield farming opportunities, and innovative blockchain applications that custodial services often can't support due to regulatory constraints.
Privacy and Censorship Resistance: These wallets allow creation without identity verification, offer enhanced transaction privacy, and resist censorship or account freezing by authorities or service providers.
Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallet: Complete Comparison
Understanding the practical differences between custodial and non-custodial wallets requires examining how each approach handles critical aspects of cryptocurrency management.
For businesses seeking middle-ground approaches, embedded wallet solutions combine elements of both custodial and non-custodial models while addressing specific regulatory compliance requirements.
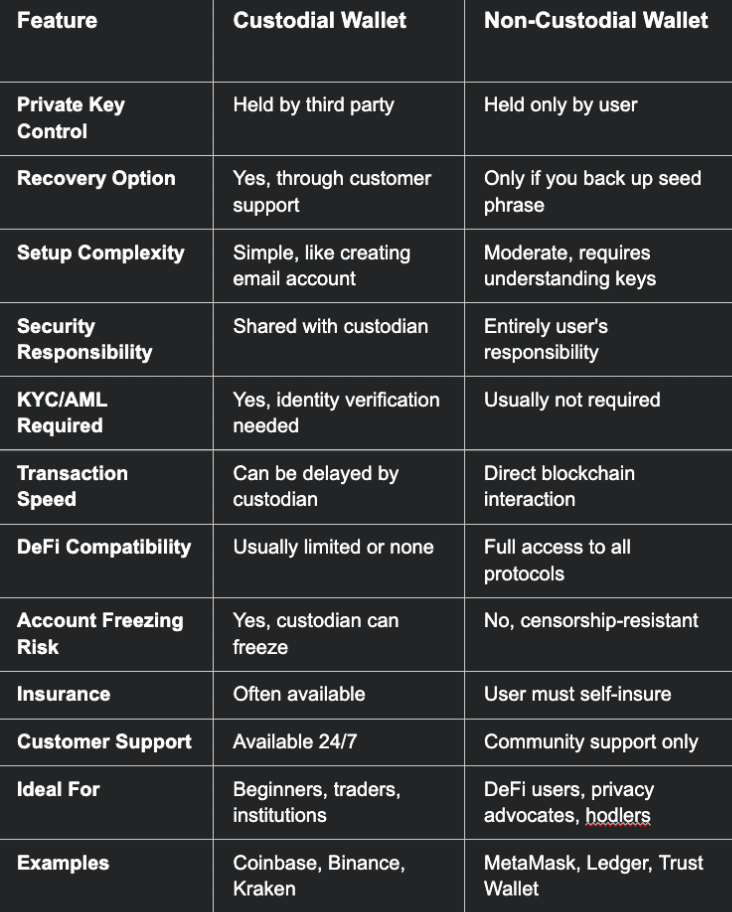
Control and Ownership Dynamics
Private Key Management represents the fundamental philosophical difference. Custodial services manage keys professionally but create dependency relationships, while non-custodial wallets provide complete sovereignty at the cost of personal responsibility.
Recovery Mechanisms illustrate practical trade-offs clearly. Custodial users benefit from account recovery through identity verification and customer support processes, while non-custodial users must rely entirely on properly stored seed phrases or face permanent fund loss.
User Experience Differences
Setup Complexity varies dramatically between approaches. Custodial wallets offer familiar account creation processes similar to email or social media platforms, while non-custodial wallets require understanding of cryptographic concepts and careful seed phrase management.
Transaction Processing differs in speed and control mechanisms. Custodial services may implement delays for security reviews or compliance checks, while non-custodial transactions proceed at blockchain speed without intermediary approval requirements.
Security Analysis: Which Wallet Type is Safer?
Security considerations represent the most critical factor in wallet selection, with 2024 data revealing important insights about cryptocurrency security risks across both custodial and non-custodial approaches.
Financial institutions must implement comprehensive digital wallet security best practices including end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and AI-driven fraud detection systems.
2025 Security Overview
According to Chainalysis research, $2.2 billion was stolen in cryptocurrency hacks during 2024, representing a 21% increase from the previous year. Understanding how these losses occurred helps inform wallet choice decisions.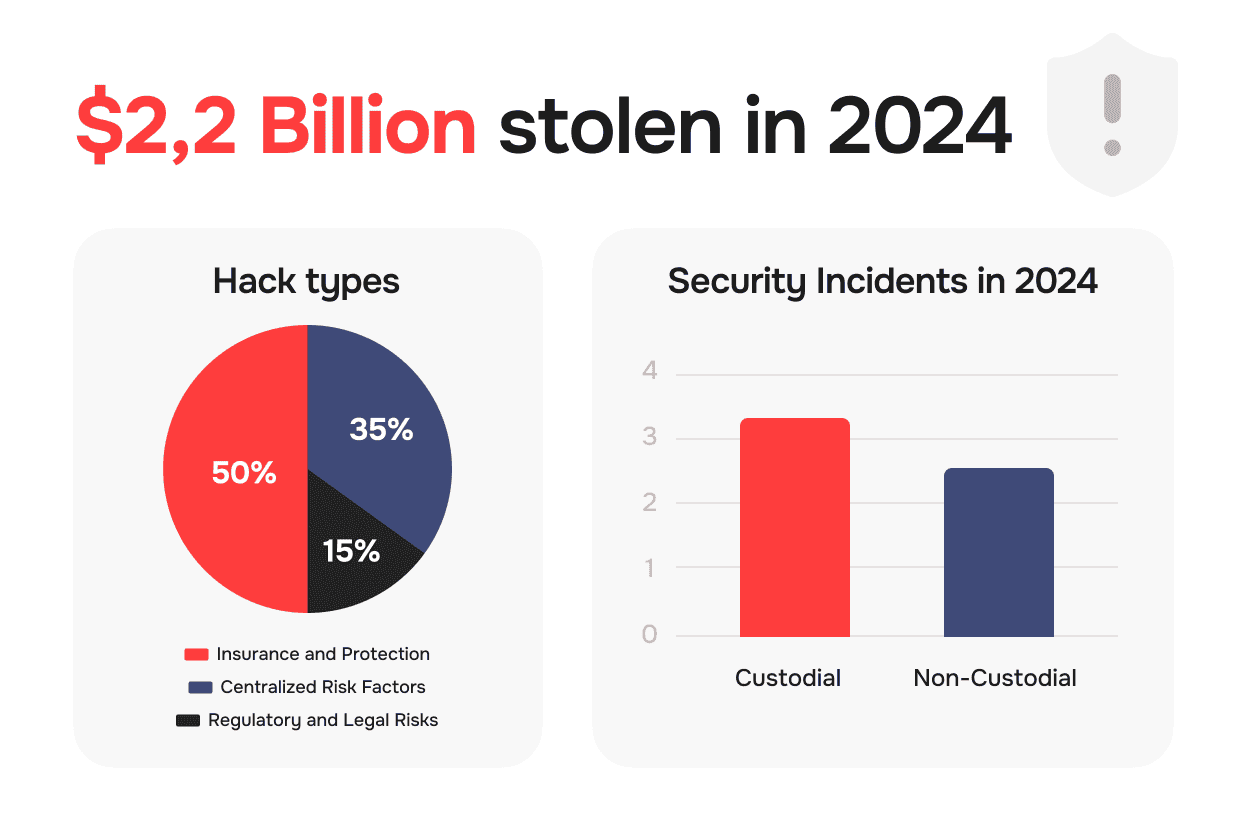
Custodial Wallet Security Profile
Professional Infrastructure Advantages: Custodial services benefit from dedicated security teams employing former government cybersecurity experts, implementing multi-layered security protocols, and undergoing regular third-party security audits. These professional measures often exceed what individual users can implement independently.
Insurance and Protection: Leading exchanges offer substantial insurance coverage, with some providing up to $250 million in protection for customer digital assets. This insurance combines FDIC coverage for fiat holdings with specialized cryptocurrency insurance policies.
Centralized Risk Factors: However, custodial services create attractive targets for attackers due to concentrated fund storage. Historical incidents demonstrate this vulnerability clearly the FTX collapse in 2022 resulted in billions in customer fund losses, while the Mt. Gox hack in 2014 led to 850,000 Bitcoin disappearing permanently.
Regulatory and Legal Risks: Government seizure represents another consideration, as authorities can freeze accounts or force asset forfeiture through legal processes, regardless of individual user innocence.
Non-Custodial Wallet Security Profile
Elimination of Counterparty Risk: Non-custodial approaches eliminate third-party risks entirely, making users immune to exchange hacks, bankruptcy, or regulatory action. Your security depends entirely on your own practices rather than external organizations.
Hardware Wallet Excellence: Hardware wallets provide exceptional security by storing private keys on air-gapped devices requiring physical confirmation for transactions. Even if your computer becomes compromised with malware, hardware wallets maintain security through isolated key storage.
User Responsibility Challenges: The primary risks involve user error and personal security failures. Lost seed phrases result in permanent fund loss with no recovery mechanism available. Malware infections can compromise software wallets, while phishing attacks trick users into revealing sensitive information.
Security Best Practices
For Custodial Users: Choose reputable, regulated exchanges with strong security track records and insurance coverage. Enable two-factor authentication, use unique passwords, and monitor accounts regularly for suspicious activity.
For Non-Custodial Users: Use reputable hardware wallets for significant amounts, store seed phrases in multiple secure physical locations, implement multi-signature configurations when possible, maintain updated wallet software, and consider using dedicated devices for cryptocurrency activities.
Security Verdict
The optimal choice depends largely on user technical competency and risk tolerance. Beginners often benefit from custodial services' professional security management and insurance coverage, while experienced users who follow proper security practices achieve superior protection through non-custodial approaches that eliminate third-party risks entirely.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrency wallets evolved significantly throughout 2024, with new compliance requirements affecting both custodial and non-custodial wallet providers across multiple jurisdictions worldwide.
Custodial Wallet Regulations
Money Service Business Requirements: Custodial wallet providers must register as Money Service Businesses (MSBs) in most jurisdictions, triggering extensive compliance obligations. These include implementing Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, maintaining Anti-Money Laundering (AML) monitoring systems, reporting suspicious transactions to authorities, and keeping comprehensive transaction records.
Travel Rule Implementation: Based on FATF Recommendation 16, custodial services must collect and share transaction information for transfers above specified thresholds, typically $1,000 or €1,000. FATF's 2024 update revealed concerning gaps, with nearly one-third of surveyed jurisdictions making insufficient progress implementing these requirements.
Insurance and Capital Standards: Regulatory frameworks increasingly require minimum capital reserves, FDIC insurance for USD holdings in the United States, and private insurance coverage for cryptocurrency assets. While these requirements provide customer protection, they also increase operational costs for service providers.
Non-Custodial Wallet Regulations
Current Regulatory Status: Non-custodial wallets remain relatively unregulated, as authorities generally treat them as software tools rather than financial services. Users typically face no KYC requirements for wallet creation and can maintain greater transaction privacy compared to custodial alternatives.
Emerging Regulatory Trends: However, new regulations are beginning to affect non-custodial users. The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, effective in 2024, introduces increased reporting requirements for large transactions. Similarly, the US infrastructure bill expanded reporting requirements for cryptocurrency transactions. European crypto service providers must navigate MiCA regulation compliance requirements, which create unified regulatory frameworks affecting both custodial and non-custodial wallet operations across EU member states.
Tax Compliance Requirements
Universal Obligations: Both wallet types create identical tax obligations for users, who remain responsible for maintaining detailed transaction records, reporting capital gains and losses accurately, and declaring income from DeFi activities regardless of their chosen wallet approach.
New IRS Requirements: A significant development for US users involves new IRS cost basis rules requiring crypto investors to switch from Universal to Per-Wallet cost basis tracking by January 1, 2025. This change affects tax calculations for both custodial and non-custodial wallet users, potentially increasing record-keeping complexity significantly.
Market Statistics and Adoption Trends
The cryptocurrency wallet market experienced remarkable expansion in 2024, driven by increasing institutional adoption, improving regulatory clarity, and expanding use cases for digital assets across various industries.
Major financial institutions like Morgan Stanley, Fidelity, and BlackRock are driving institutional digital asset adoption, with 51% of institutional investors maintaining positive perceptions of digital assets despite market volatility.
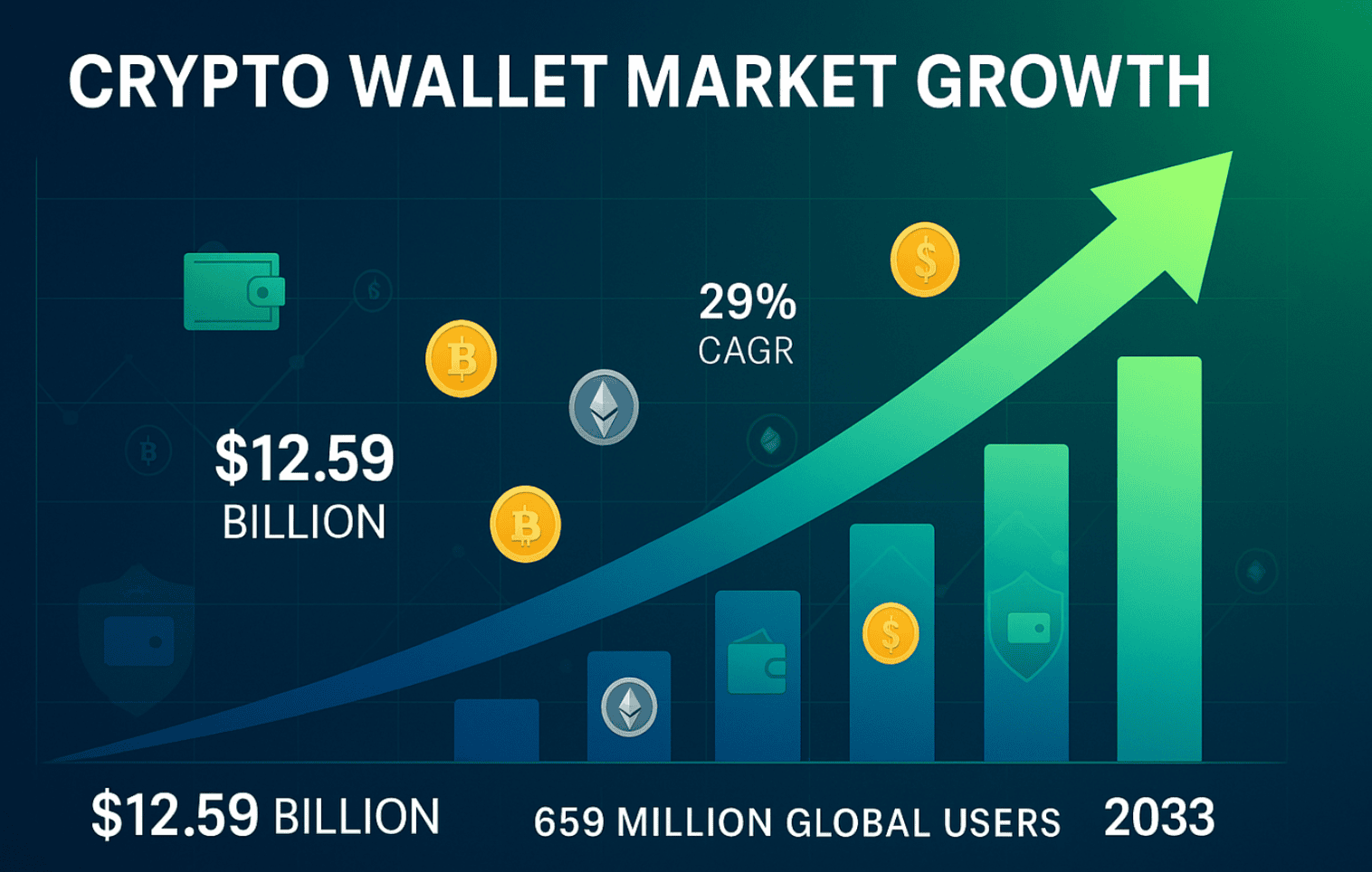
Global Market Growth
Market Size Expansion: The total crypto wallet market reached $12.59 billion in 2024 with projections indicating growth to $100.77 billion by 2033, representing a compound annual growth rate of 26.3%. This impressive growth reflects not only increased user adoption but also the maturation of wallet technology and enhanced security features.
User Adoption Statistics: Global cryptocurrency ownership reached 659 million users as of 2024, representing a 13% increase from the previous year. This translates to approximately 6.8% global cryptocurrency ownership rate, with mobile crypto wallets achieving a record high of 36 million active wallets in the fourth quarter alone.
Market Segmentation Trends
Non-Custodial Growth: The non-custodial wallet market, valued at $1.5 billion in 2023, projects growth to $8.4 billion by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 24.3%. This acceleration indicates increasing user sophistication and growing desire for self-custody solutions.
Regional Adoption Patterns: Central and Southern Asia and Oceania lead global cryptocurrency adoption according to Chainalysis's 2024 Global Crypto Adoption Index. Developing markets often show higher adoption rates due to currency instability, limited traditional banking access, and younger, tech-savvy populations.
Institutional Adoption Impact
Professional Market Entry: Traditional financial institutions increasingly offer cryptocurrency custody services and wallet solutions, validating the market while driving professionalization of custody practices and security standards. This institutional entry provides legitimacy and attracts previously skeptical corporate and individual users.
DeFi Integration: Decentralized Finance protocols reached 27.3 million unique wallet addresses in 2024, highlighting the growing importance of non-custodial wallets for accessing yield farming, liquidity provision, and other advanced financial services unavailable through traditional custodial platforms.
When to Use Custodial Wallets
Custodial wallets excel in specific scenarios where convenience, support, and integrated services outweigh the trade-offs of third-party control over private keys.
Large enterprises and financial institutions requiring professional-grade security should evaluate whether to build or buy institutional crypto custody solutions, with most finding third-party providers more cost-effective than internal development.
Ideal User Profiles
Cryptocurrency Beginners: New users benefit significantly from custodial wallets' familiar user interfaces, comprehensive customer support, and built-in educational resources. The learning curve for understanding private keys, seed phrases, and blockchain interactions can overwhelm newcomers, making custodial services an excellent entry point.
Active Traders: Frequent traders appreciate integrated exchange functionality, advanced trading tools, and instant access to multiple cryptocurrency pairs. Custodial platforms typically offer superior liquidity, margin trading capabilities, and professional-grade charting tools unavailable in basic non-custodial wallets.
Business and Institutional Users: Companies requiring accounting integration, compliance reporting, and multi-user access controls find custodial solutions better suited to their operational needs. These platforms often provide APIs, detailed transaction histories, and regulatory reporting tools essential for business use.
Specific Use Cases
Regulatory Compliance Needs: Users in heavily regulated industries or jurisdictions may require the KYC/AML compliance, transaction monitoring, and reporting capabilities that custodial services provide by default.
Customer Support Requirements: Individuals who value having human support available for technical issues, account problems, or transaction disputes benefit from custodial platforms' comprehensive customer service infrastructure.
Integrated Financial Services: Users interested in earning yield through staking, lending, or savings products often find custodial platforms offer more user-friendly access to these services compared to navigating complex DeFi protocols independently.
