Digital Identity Management: Securing the Future of Finance
As financial services embrace digital transformation, identity management has become the cornerstone of secure, compliant, and user-friendly financial experiences. With financial fraud losses reaching $47 billion in 2024 and data breaches costing the financial sector an average of $6.08 million per incident, the stakes have never been higher.
The convergence of traditional finance and blockchain technology is creating unprecedented opportunities and challenges in digital identity management. From decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols to institutional custody solutions, the financial industry is grappling with how to verify, authenticate, and protect user identities in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
This comprehensive analysis explores the current state of digital identity management in finance, examines emerging trends and technologies, and provides actionable strategies for building secure, scalable identity systems that meet today's regulatory requirements while preparing for tomorrow's innovations.
The Current State of Digital Identity in Finance
Digital identity management in financial services has evolved from simple username-password combinations to sophisticated multi-factor authentication systems, biometric verification, and blockchain-based identity solutions. However, this evolution has come with significant growing pains.
The Cost of Identity Fraud
Recent data reveals the staggering financial impact of identity-related security failures. According to Javelin Strategy & Research, American adults lost $47 billion to identity fraud and scams in 2024, representing a $4 billion increase over 2023. This upward trend reflects both the sophistication of modern attack vectors and the increasing digitization of financial services.
For financial institutions, the direct costs are equally concerning. Research from Entrust and DocuSign indicates that organizations face an average of $7 million in annual identity fraud costs, with larger enterprises bearing an even heavier burden. Companies with over 5,000 employees report average annual direct identity fraud costs of $13 million.
The ripple effects extend beyond immediate financial losses. Cybersecurity incidents involving identity compromise affect 43% of businesses, with 48% experiencing multiple incidents annually. These breaches damage customer trust, trigger regulatory scrutiny, and require substantial remediation investments.
Regulatory Pressure and Compliance Challenges
The regulatory landscape for digital identity management is becoming increasingly complex and stringent. The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which took full effect in 2024, exemplifies this trend by establishing comprehensive identity verification requirements for crypto asset service providers.
Similarly, the EU Travel Rule mandates that crypto asset service providers share detailed sender and recipient information for transactions, creating new challenges for privacy-focused blockchain applications. These regulations reflect a global shift toward enhanced transparency and accountability in digital financial services.
As discussed in our analysis of MiCA's impact on crypto providers, compliance with these evolving requirements demands sophisticated identity management systems that can adapt to changing regulatory frameworks while maintaining operational efficiency.
Blockchain and Web3 Identity Solutions
The blockchain identity management market is experiencing explosive growth, with the global market valued at $3.38 billion in 2023 and projected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) exceeding 50% through 2032. Financial services currently command the largest market share at 31.48%, reflecting the sector's urgent need for secure, scalable identity solutions.
Decentralized Identity: Promise and Challenges
Decentralized identity systems offer compelling advantages over traditional centralized approaches. By giving users control over their identity data and eliminating single points of failure, these systems can enhance both security and privacy. The decentralized identity market is projected to reach an extraordinary $1.17 trillion by 2035, growing at an 87.43% CAGR.
However, the reality of implementing decentralized identity in regulated financial services is more complex. Financial institutions must balance user autonomy with regulatory requirements for customer due diligence and anti-money laundering compliance. This tension has led to the development of hybrid approaches that combine decentralized architecture with compliant identity verification processes.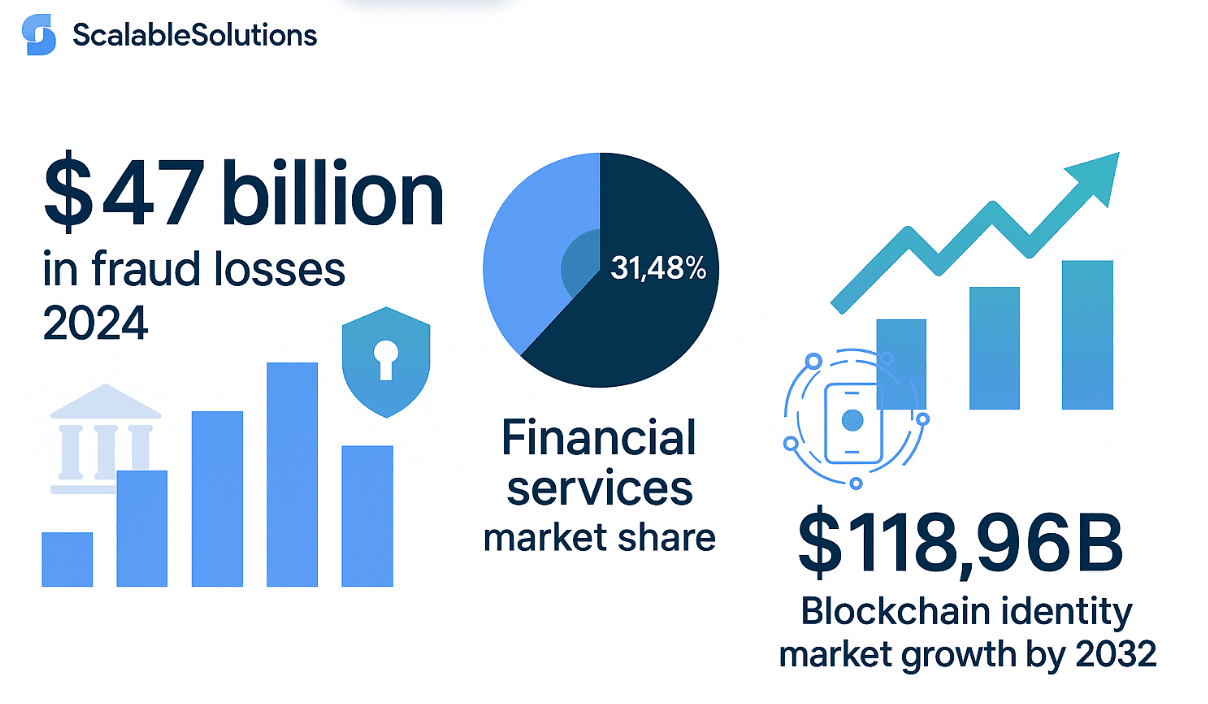
Smart Contracts and Automated Compliance
Smart contracts are emerging as powerful tools for automating identity verification and compliance processes. By encoding regulatory requirements directly into blockchain protocols, financial institutions can create self-executing compliance systems that reduce manual oversight while ensuring consistent rule enforcement.
This approach is particularly valuable in DeFi applications, where traditional KYC/AML processes must be adapted for decentralized environments. Smart contracts can automatically verify user credentials, check sanctions lists, and trigger additional verification steps when required, all while maintaining user privacy through zero-knowledge proofs and other cryptographic techniques.
Security Technologies and Infrastructure
The foundation of effective digital identity management lies in robust security infrastructure. As financial institutions navigate the choice between different security approaches, understanding the trade-offs between various technologies becomes crucial.
Multi-Party Computation vs. Hardware Security Modules
The debate between Multi-Party Computation (MPC) and Hardware Security Modules (HSM) for securing digital identities and cryptographic keys reflects broader questions about distributed versus centralized security models. As explored in our detailed comparison of MPC vs. HSM for custody solutions, each approach offers distinct advantages.
MPC distributes cryptographic operations across multiple parties, eliminating single points of failure and enabling flexible, scalable security architectures. This approach is particularly well-suited to Web3 applications where decentralization is a core principle. However, MPC systems require sophisticated coordination mechanisms and may face performance challenges in high-throughput environments.
HSMs, by contrast, provide hardware-backed security guarantees and have established track records in traditional financial services. They offer superior performance for cryptographic operations and well-understood certification processes. However, HSMs represent centralized points of failure and may limit the scalability and flexibility of identity management systems.
Biometric Authentication and AI Integration
Biometric authentication is becoming increasingly sophisticated, with AI-powered systems capable of detecting deepfakes and other advanced spoofing attempts. However, this arms race between authentication technologies and attack methods requires constant vigilance and investment.
The integration of artificial intelligence into identity verification systems offers both opportunities and risks. AI can enhance fraud detection capabilities, automate risk assessment, and provide adaptive authentication that adjusts security requirements based on user behavior and transaction context. However, AI systems also introduce new attack vectors, including adversarial machine learning attacks that could compromise identity verification processes.
DeFi and Digital Identity Challenges
Decentralized Finance presents unique challenges for digital identity management. The pseudonymous nature of blockchain transactions conflicts with traditional financial regulations that require customer identification and monitoring. This fundamental tension has led to innovative approaches for reconciling privacy with compliance.

Privacy-Preserving Compliance
Zero-knowledge proofs and other privacy-preserving technologies enable users to prove their identity or compliance status without revealing sensitive personal information. These cryptographic techniques allow DeFi protocols to verify that users meet regulatory requirements (such as accredited investor status or jurisdictional eligibility) without compromising user privacy.
However, implementing these technologies at scale remains challenging. Privacy-preserving compliance systems require significant computational resources, complex key management, and careful design to prevent information leakage through side channels.
Cross-Chain Identity Management
As DeFi ecosystems span multiple blockchain networks, managing identity across different chains becomes increasingly complex. Users may have different identities, reputation scores, and compliance statuses on different networks, creating fragmentation that hampers user experience and regulatory oversight.
Emerging solutions include cross-chain identity protocols that enable users to maintain consistent identities across multiple blockchain networks. These systems typically rely on bridge protocols or shared identity registries to synchronize identity information across chains while maintaining security and decentralization principles.
Custody and Wallet Security Considerations
The choice between custodial and non-custodial wallet architectures has profound implications for digital identity management. As outlined in our comprehensive analysis of digital wallet security for banks, each approach presents distinct trade-offs between security, compliance, and user control.
Custodial Solutions: Centralized Security
Custodial wallet solutions offer clear advantages for regulatory compliance and security management. Financial institutions can implement comprehensive identity verification processes, monitor transactions for suspicious activity, and maintain detailed audit trails. This centralized approach aligns well with existing banking practices and regulatory expectations.
However, custodial solutions also create single points of failure and may limit user autonomy. The recent security breaches affecting major exchanges underscore the risks associated with centralized custody models. When evaluating custodial solutions, institutions must consider not only their own security practices but also the robustness of their service providers' infrastructure.
Non-Custodial Approaches: User Sovereignty with Compliance Challenges
Non-custodial wallets give users direct control over their private keys and funds, potentially enhancing security by eliminating centralized points of failure. However, this approach complicates identity management and regulatory compliance, as financial institutions have limited visibility into user activities and wallet security practices.
The emergence of embedded wallet solutions offers a potential middle ground, combining user control with institutional oversight. These systems can provide graduated levels of custody, allowing users to manage smaller amounts independently while requiring institutional involvement for larger transactions or high-risk activities.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Effective digital identity management must navigate an increasingly complex regulatory landscape while maintaining operational efficiency and user experience. The challenge is compounded by the global nature of digital finance, which requires compliance with multiple, sometimes conflicting, regulatory frameworks.
Global Regulatory Convergence and Divergence
While some aspects of financial regulation are converging globally, significant differences remain in approaches to digital identity and privacy. The European Union's emphasis on data protection through GDPR contrasts with other jurisdictions' focus on financial transparency and anti-money laundering.
These regulatory differences create challenges for global financial service providers, who must implement identity management systems that can adapt to different compliance requirements based on user location, transaction type, and regulatory jurisdiction. Our analysis of regulatory compliance for custody solutions explores these challenges in detail.
Risk-Based Authentication
Modern identity management systems increasingly rely on risk-based authentication that adjusts verification requirements based on transaction context, user behavior, and assessed risk levels. This approach can improve user experience by reducing friction for low-risk activities while maintaining strong security for high-risk transactions.
Implementing effective risk-based authentication requires sophisticated analytics capabilities, real-time decision-making systems, and careful calibration to avoid both false positives and false negatives. Machine learning algorithms can enhance these systems by identifying subtle patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity, but they also require ongoing monitoring and adjustment to remain effective.
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
The digital identity management landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological innovation, regulatory changes, and shifting user expectations. Several key trends are likely to shape the future of identity management in financial services.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML technologies are becoming integral to identity verification and fraud prevention systems. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify suspicious patterns, automate risk assessment processes, and provide real-time authentication decisions. However, they also introduce new vulnerabilities, including adversarial attacks and algorithmic bias.
The integration of AI into identity management systems requires careful consideration of explainability, fairness, and robustness. Financial institutions must ensure that their AI-powered systems can provide clear explanations for identity decisions, treat all users fairly regardless of demographic characteristics, and remain effective in the face of evolving attack strategies.
Quantum Computing Implications
The potential advent of practical quantum computing poses both opportunities and threats for digital identity management. Quantum computers could render current cryptographic standards obsolete, requiring migration to quantum-resistant algorithms. However, quantum technologies also offer new possibilities for secure communication and authentication.
Financial institutions should begin preparing for the quantum transition by evaluating their cryptographic dependencies, planning migration strategies, and staying informed about quantum-resistant standards development. This preparation is particularly important for long-term identity management systems that may need to maintain security over decades.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Building effective digital identity management systems requires a strategic approach that balances security, compliance, user experience, and operational efficiency. Based on industry experience and emerging best practices, several key principles should guide implementation efforts.
Identity-First Architecture
Successful digital identity management begins with treating identity as a foundational architectural component rather than an add-on feature. This identity-first approach requires careful consideration of identity data models, authentication flows, and access control mechanisms from the earliest stages of system design.
Identity-first architecture also emphasizes interoperability and standards compliance, ensuring that identity systems can integrate with existing infrastructure while remaining flexible enough to accommodate future requirements. This approach is particularly important in hybrid environments that combine traditional banking systems with blockchain-based applications.
Progressive Enhancement and Gradual Migration
Rather than attempting wholesale replacement of existing identity systems, many successful implementations follow a progressive enhancement strategy that gradually introduces new capabilities while maintaining compatibility with legacy systems. This approach reduces implementation risk and allows organizations to gain experience with new technologies before committing to large-scale deployments.
Progressive enhancement strategies typically begin with low-risk use cases, such as customer onboarding for new products or authentication for non-critical services. As confidence and capability grow, organizations can expand the scope of their identity management systems to cover more critical functions.
Multi-Layered Security Approach
Effective identity management relies on defense in depth, implementing multiple layers of security controls rather than depending on any single technology or process. This multi-layered approach should include technical controls (such as encryption and access controls), procedural controls (such as identity verification processes), and physical controls (such as secure hardware).
The specific combination of security layers will depend on the organization's risk profile, regulatory requirements, and operational constraints. However, all implementations should include mechanisms for monitoring, alerting, and incident response to ensure that security breaches are detected and addressed quickly.
Measuring Success and ROI
Evaluating the effectiveness of digital identity management systems requires clear metrics and benchmarks that align with business objectives and risk management goals. Organizations should establish baseline measurements before implementing new systems and track progress against these baselines over time.
Security Metrics
Key security metrics for digital identity management include the number and severity of identity-related incidents, time to detect and respond to security breaches, and the effectiveness of fraud prevention measures. Organizations should also track false positive and false negative rates for their authentication systems to ensure that security measures don't unduly impact user experience.
Operational Efficiency
Identity management systems should also be evaluated based on their impact on operational efficiency. Metrics might include the time required for customer onboarding, the cost per identity verification, and the level of manual intervention required for identity-related processes. Automation and streamlining of identity management processes can provide significant cost savings over time.
Compliance and Risk Reduction
The value of effective identity management extends beyond direct cost savings to include risk reduction and compliance benefits. Organizations should track regulatory compliance metrics, such as the completeness and accuracy of customer due diligence records, as well as risk indicators, such as the number of suspicious activity reports filed and the results of regulatory examinations.
Conclusion: Building the Foundation for Digital Finance
Digital identity management has emerged as the critical foundation for the future of finance. As the industry continues its digital transformation, the ability to securely verify, authenticate, and manage user identities will determine the success of financial institutions, fintech innovators, and blockchain-based applications alike.
The statistics are clear: with $47 billion in annual fraud losses and average data breach costs of $6.08 million in the financial sector, the stakes of getting identity management right have never been higher. Yet the opportunities are equally significant, with the blockchain identity management market growing at over 50% annually and new technologies offering unprecedented capabilities for secure, privacy-preserving identity verification.
Key Takeaways for Financial Industry Leaders
Embrace a Strategic Approach: Digital identity management requires comprehensive strategy that considers technology, regulation, user experience, and business objectives. Organizations that treat identity as a foundational architectural component will be better positioned for long-term success.
Invest in Emerging Technologies: Blockchain-based identity solutions, AI-powered fraud detection, and privacy-preserving authentication technologies offer significant advantages for organizations willing to invest in their development and deployment.
Prepare for Regulatory Evolution: The regulatory landscape for digital identity continues to evolve rapidly. Organizations must build flexible compliance capabilities that can adapt to changing requirements while maintaining operational efficiency.
Balance Security and Usability: Effective identity management systems must provide robust security without creating barriers to user adoption. Risk-based authentication and progressive enhancement strategies can help achieve this balance.
Plan for the Long Term: Digital identity infrastructure decisions made today will impact organizations for years to come. Consider future requirements, including quantum computing implications and evolving threat landscapes, when designing identity management systems.
The financial industry stands at a crucial juncture in the evolution of digital identity management. Organizations that act decisively to implement secure, compliant, and user-friendly identity systems will gain competitive advantages that extend far beyond mere regulatory compliance. They will build the foundation for innovative financial products, enhanced customer experiences, and sustainable growth in the digital economy.
At Scalable Solutions, we understand these challenges intimately. With 12 years of experience in financial technology and zero security breaches over that period, we've helped institutions navigate the complex landscape of digital identity management while maintaining the highest standards of security and compliance. Whether you're exploring regulatory compliance strategies or implementing cutting-edge custody solutions, the foundation of success lies in robust, thoughtfully designed digital identity management systems.
The future of finance is digital, decentralized, and global. The organizations that master digital identity management today will be the ones that shape that future tomorrow.


